Visiting a website is a bit like going on a date.
You show up on a page and hope the content will perfectly match your expectations.
In many cases, the magic isn’t quite there, but just occasionally, you find the one — the only article you’ll ever need on cooking with chorizo (everyone loves a good sausage).
Wait, there’s a problem. The link to the best chorizo supplier in the world is broken! If this were an actual date, you would’ve been ghosted.
That’s exactly how visitors to your website feel when they come across broken links. It’s a painful experience that only time (and website maintenance) can heal.
If you want to prevent this kind of heartbreak and make every customer fall in love with your brand, this is your super simple guide to finding and fixing broken links.
Why Broken Links Are Bad News for Business
When your site contains broken links, visitors will come across 404 errors when they try to navigate.
This might sound like a relatively minor issue in the grand scheme of your website, but some major consequences can really harm your business.
Broken Links Create a Bad User Experience
When someone clicks a link, it’s because they really want to visit a certain page.
If access is denied because a link is broken, your visitors can quickly become frustrated. It can be enough to make them bounce (leave your site) and never return.

Broken Links Can Damage Your Brand Reputation
If you visited a brick-and-mortar store and found spiders’ webs in the corners, you’d probably think twice about sticking around.
Broken links create exactly the same off vibe on your website. It feels like the place has been neglected and allowed to fall into ruin.
Broken Links Could Prevent Conversions
Some links on your website are really important — stuff like your CTAs (calls to action) and menu items. If these elements break, customers who are ready to convert could be unable to follow through.
The likely result is a big negative impact on your total number of sales or sign-ups.
Broken Links Harm Your SEO Efforts
If you’re trying to climb the search rankings, you can’t afford to carry too many dead links.
There’s a list of reasons why:
- When visitors bounce because of a bad user experience, search engines take note.
- Broken links also distract search engine crawler bots from the task of mapping your site.
- Search engines will mark down your domain authority if they see enough broken links.
- They’ll also assume your site is a deserted wasteland that’s not worth visiting.
In other words — no bueno.
So, What Causes Broken Links?
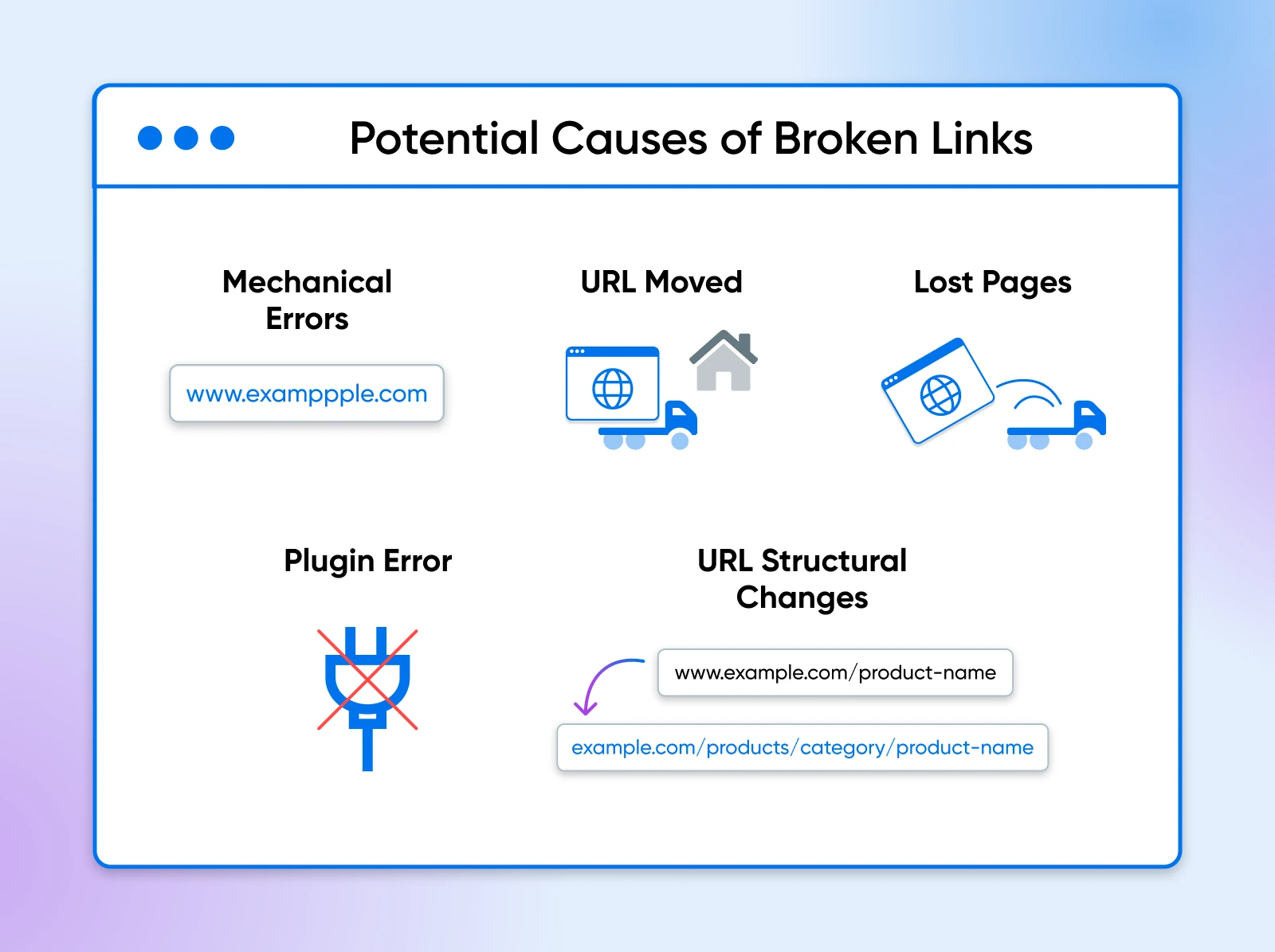
A link is broken — or “dead” — when it points to a page that doesn’t exist. This problem occurs for a variety of reasons:
- Typographical errors: When you created the URL, it’s possible you made a whoopsie. Common errors include missing the “https://” or adding extra spaces.
- URL updates: You got the URL right at the time but the page has moved to a new home. This can cause problems if there are no proper URL redirects in place.
- Lost pages: When content is deleted or moved, you can end up seeing a 404 page.
- Malfunctioning plugins: Misbehaving add-ons can set up HTML or JavaScript errors, which may break certain elements — like your links.
- Changes in URL structures: While the specific page URL might remain the same, changes to the overall structure of site URLs can still break things (e.g. “example.com/product-name” changing to “example.com/products/category/product-name”).
So many things could cause broken links, no wonder you have some!
5 Ways To Track Down and Fix Broken Links
You’re here ’cause you found some broken links on your site, right?
While you could just fix those specific instances, we recommend checking your entire site for problem links. That way, none will slip through the net.
Here are the best ways to find broken links, starting with the easiest option known to humankind…
1. Use a Broken Link Checker Tool
Well…this one is kinda obvious.
Specialized tools like the W3C Link Checker and Ahrefs’ Broken Link Checker are free and effective. Simply type in your website URL and wait a few minutes while the tool performs a link check.
You should then get a complete list of links that need updating. But…here’s the bad news: you now need to update these manually — one by one.
That means fixing typos, moving to the new URL for a particular page, or removing the link completely.
2. Install a Broken Link Checker WordPress Plugin
If your site runs on the world’s favorite CMS, you’re in luck. There are loads of great plugins that can find broken links on your site, and help you fix them.
The accurately named Broken Link Checker is the standout option here. It allows you to scan your entire site with a click, and then edit the individual URLs from the results page.
Here’s how to set it up:
Head to Plugins > Install New Plugin in your WordPress admin area.
Search for “Broken Link Checker.” It’s the one that looks like this:
Hit Install Now. Once that process is complete, click Activate.
Next, find the new “Link Checker” option in the WordPress sidebar. Click it, and you’ll be presented with two options:
- Cloud (new): This uses remote servers to handle link checking, taking the pressure off your host, which can be good on larger sites. It’s also more comprehensive. The downside is that you’ll need to create a free account.
- Local (old): This starts a search locally. This works fine for most SMB websites, but it relies on your host’s servers.
The plugin will run a scan on your site and reveal how many broken links you have. If you choose the “Cloud” option, you will need to click VIEW FULL REPORT to see them.
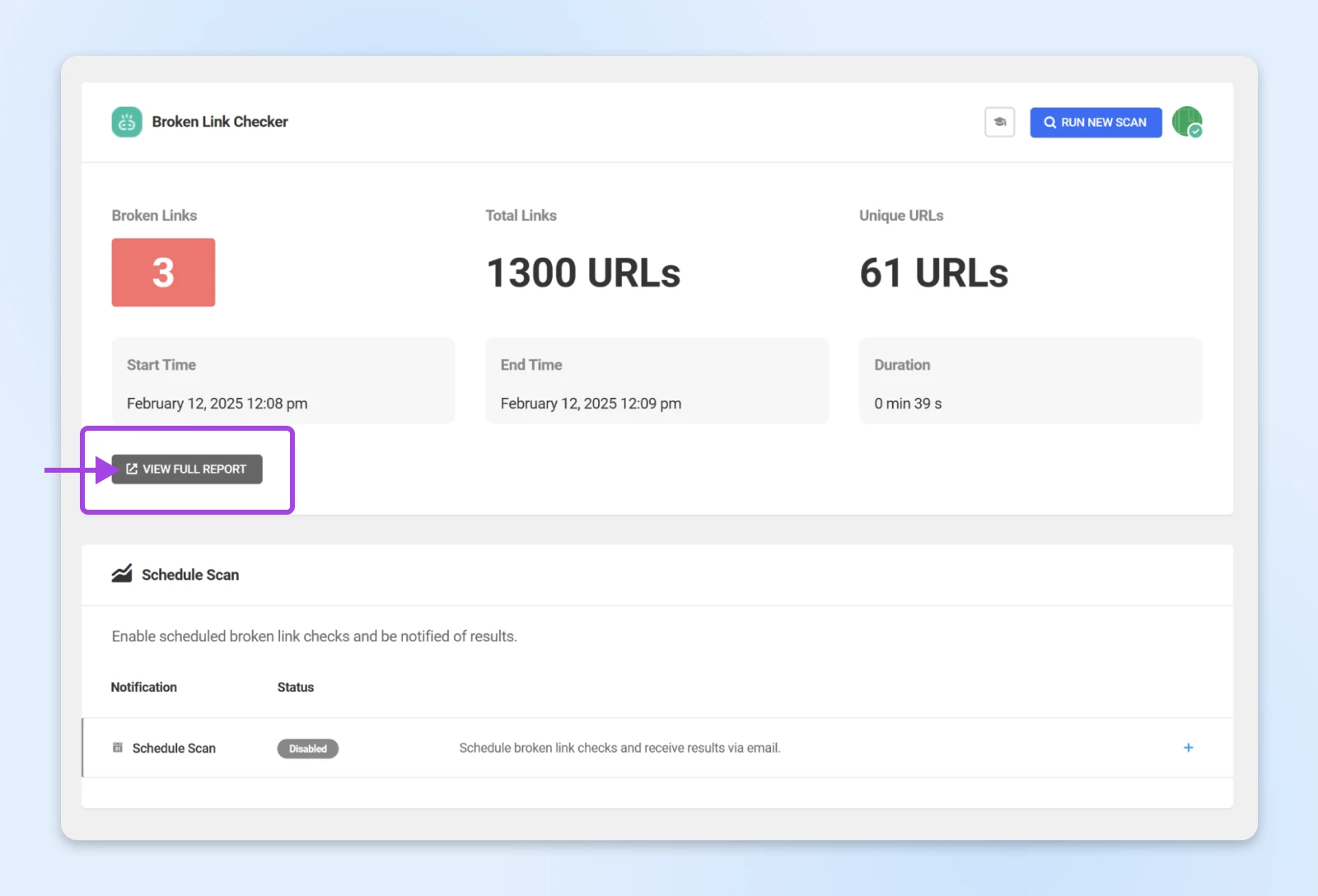
On the results page, tap Edit Link next to each broken link to make your fix.
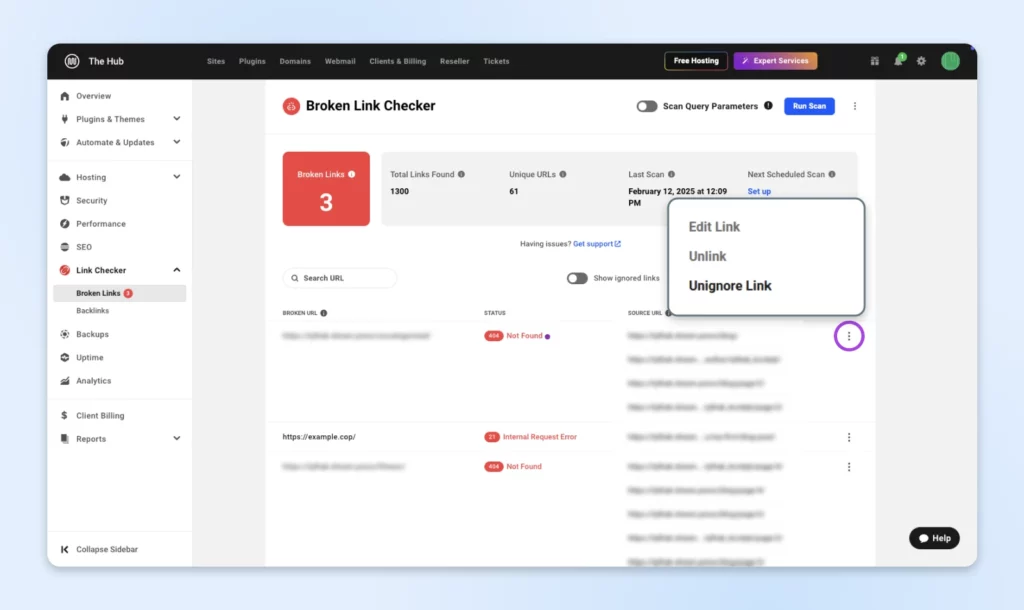
If you’re using WordPress, a plugin’s the quickest way to patch up those broken links.
3. Check Google Search Console’s Crawl Errors Report
Given the SEO impacts of broken links, it’s a good idea to get Google’s view on your website. You can do this by visiting Google Search Console (GSC).
While GSC will provide similar results to the tools mentioned above, it can reveal additional insights about broken links and help you figure out which links to fix first.
Here’s the workflow:
Visit GSC and click on Settings in the sidebar.
Next, scroll down until you see “Crawl stats.” Hit the OPEN REPORT button here.
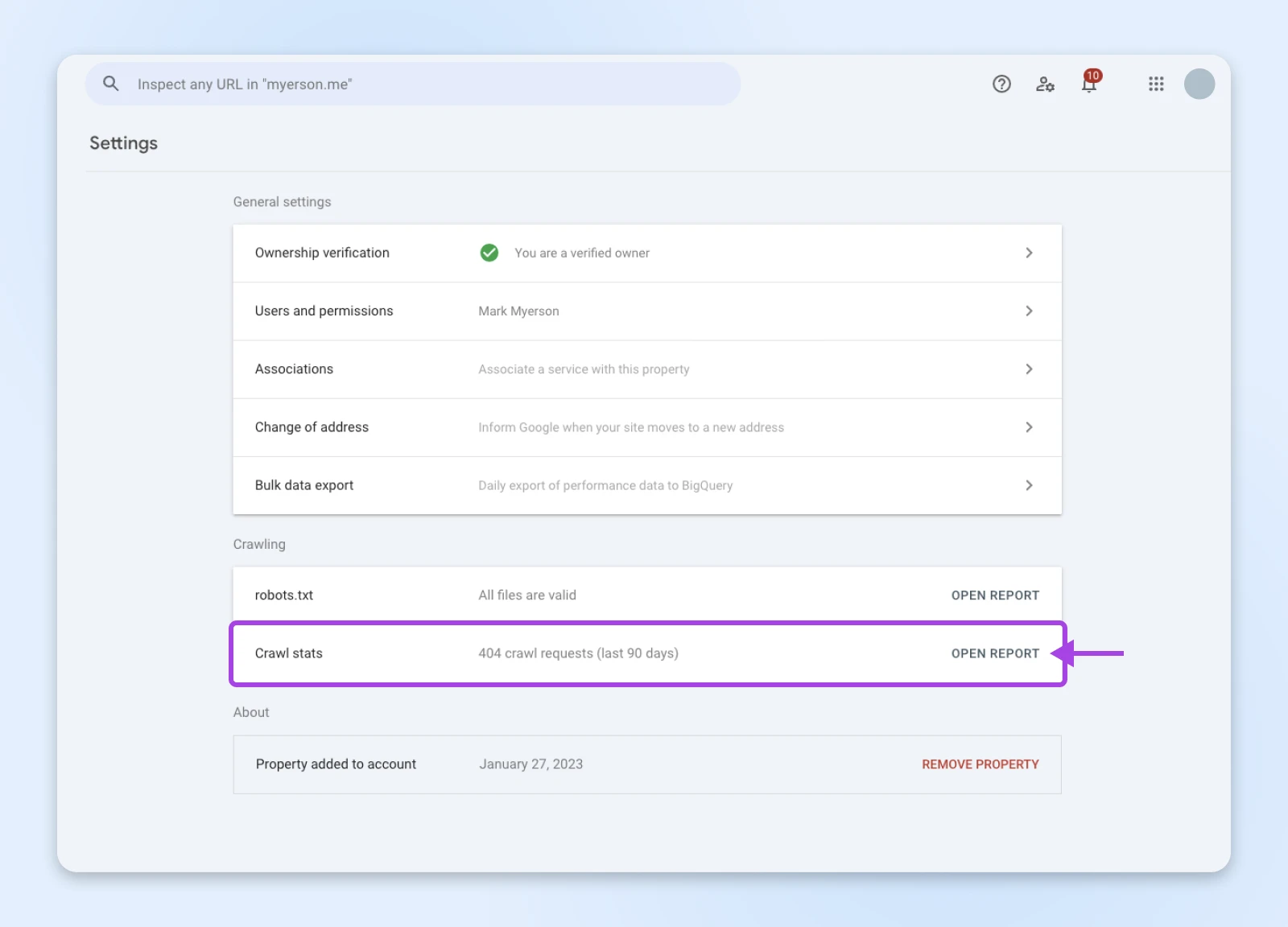
Ooh, lots of nice data – but we just need the “By response” box.
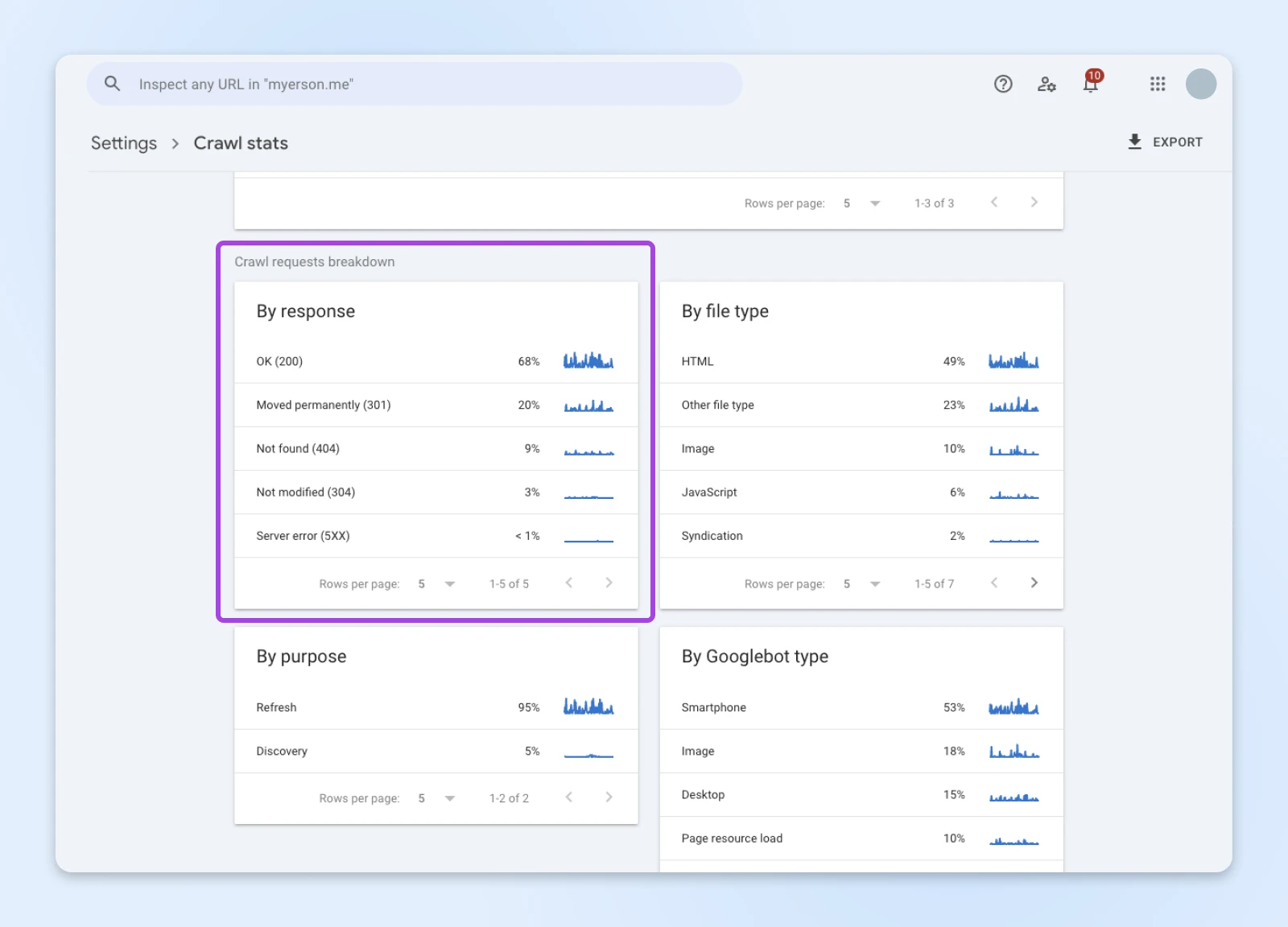
Start by tapping on Not found (404) from the list. Google should provide a complete list of links that produce a 404 error page. You’ll need to fix these on your website.
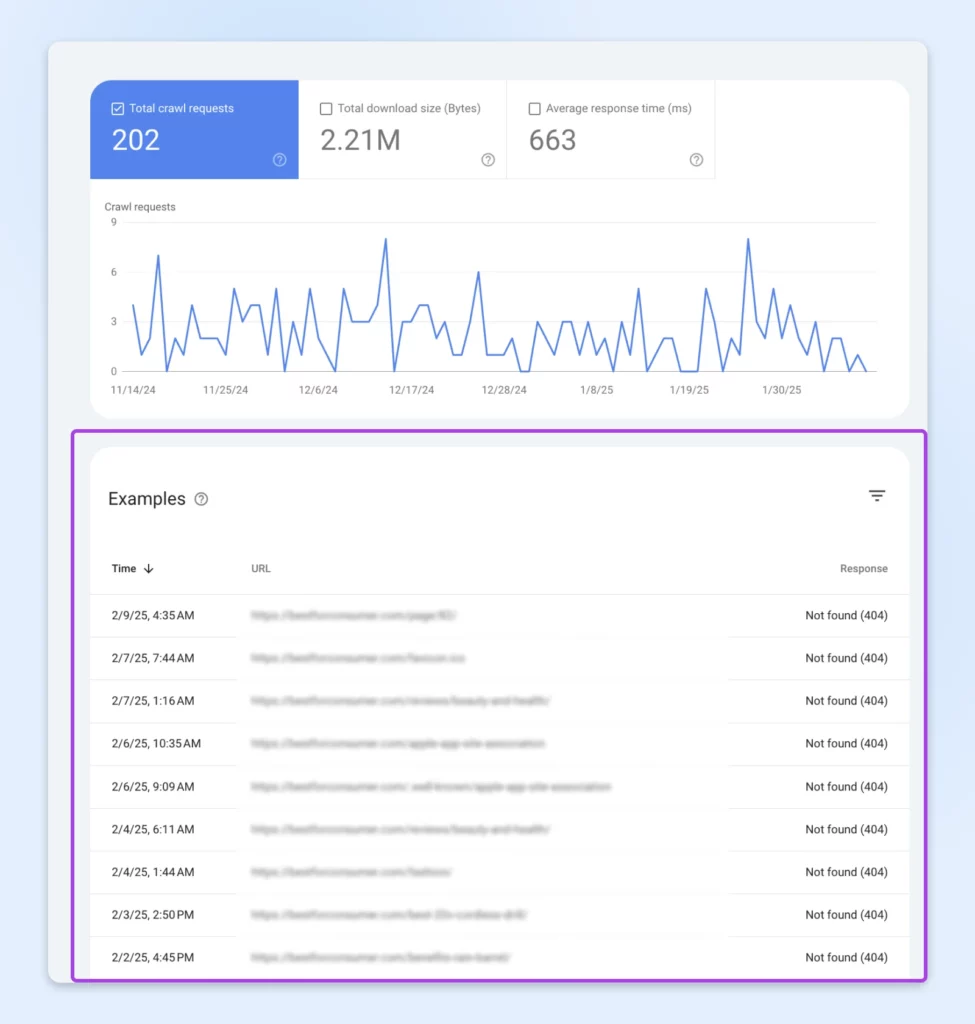
Now, return to the previous screen and select Moved permanently (301). These broken links point to pages that have moved to new pastures. You need to fix these as well (more on this in the next section).
One advantage of using GSC is that you can easily see recurring problems over time, such as redirects…
4. Implement 301 Redirects
Whenever you make a significant change to your website, such as migrating to a new host or changing the domain name, the URL for each page is likely to change.
If you don’t rectify the problem, links to your content will break, and users will encounter a 404 error.
The solution is to use 301 redirects. These instructions help web browsers to find the new location for existing content. It’s like hanging a “We’ve moved!” sign on your shop window.
There are two ways to set up 301 redirects:
- Using a plugin (easy)
- By editing your .htaccess file (a bit more technical)
If your site runs on WordPress, we recommend using a plugin like Safe Redirect Manager. Here’s how to get started:
In your WordPress admin area, hit Plugins > Add New Plugin.
Search for “Safe Redirect Manager.” This is the one you want:
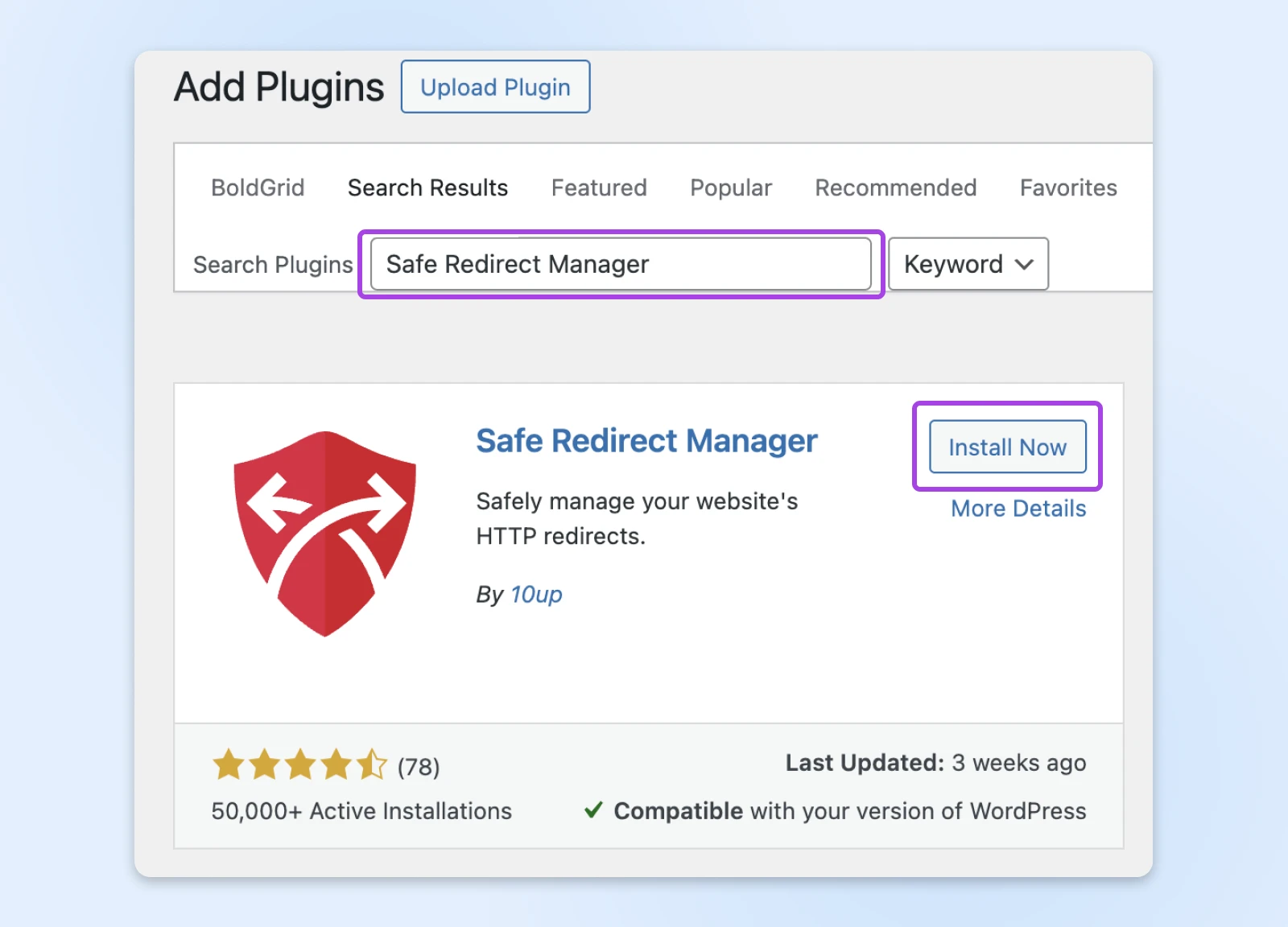
Select Install Now, and then Activate when it appears.
Make your way to Tools > Safe Redirect Manager.
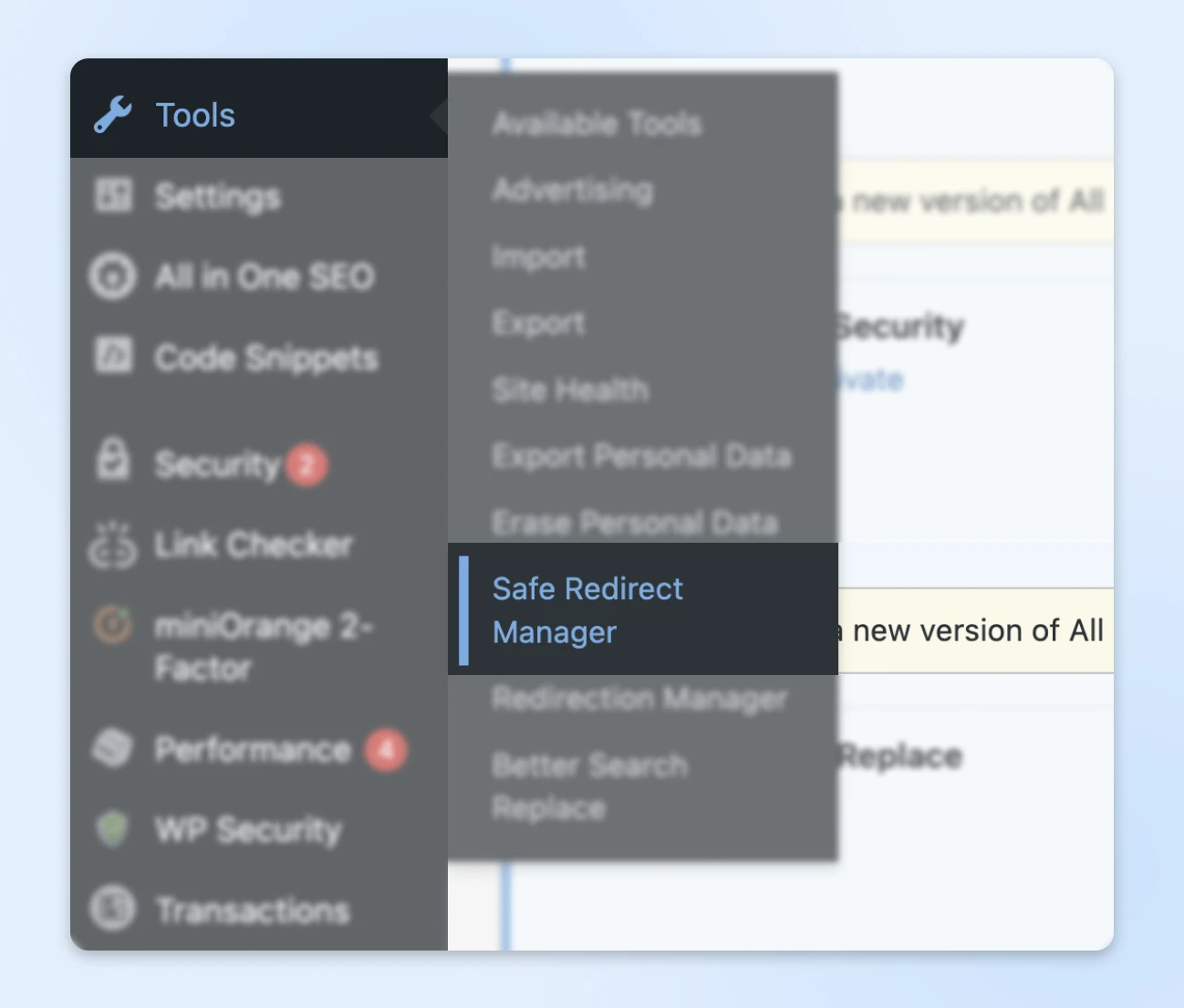
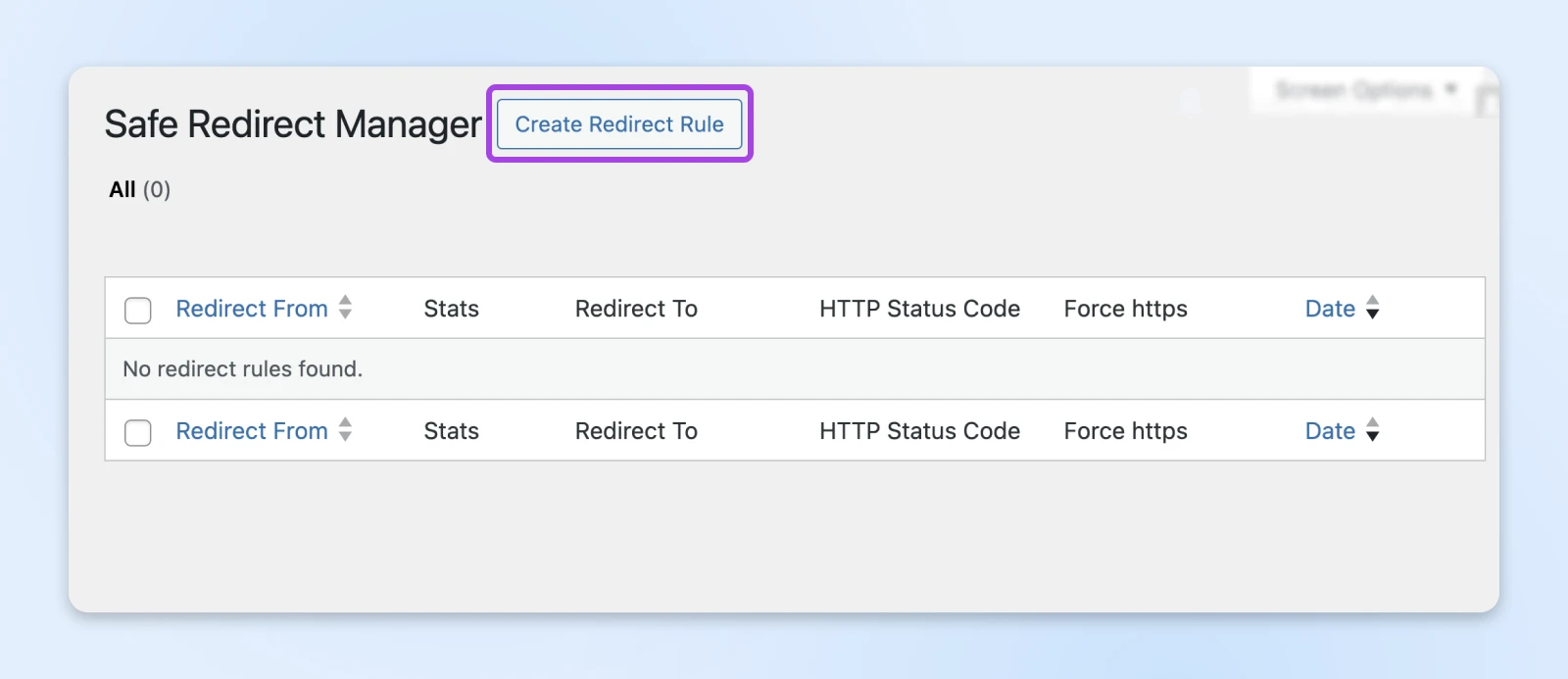
Here, you can start setting up redirects for the URLs that have moved. Just hit Create Redirect Rule.
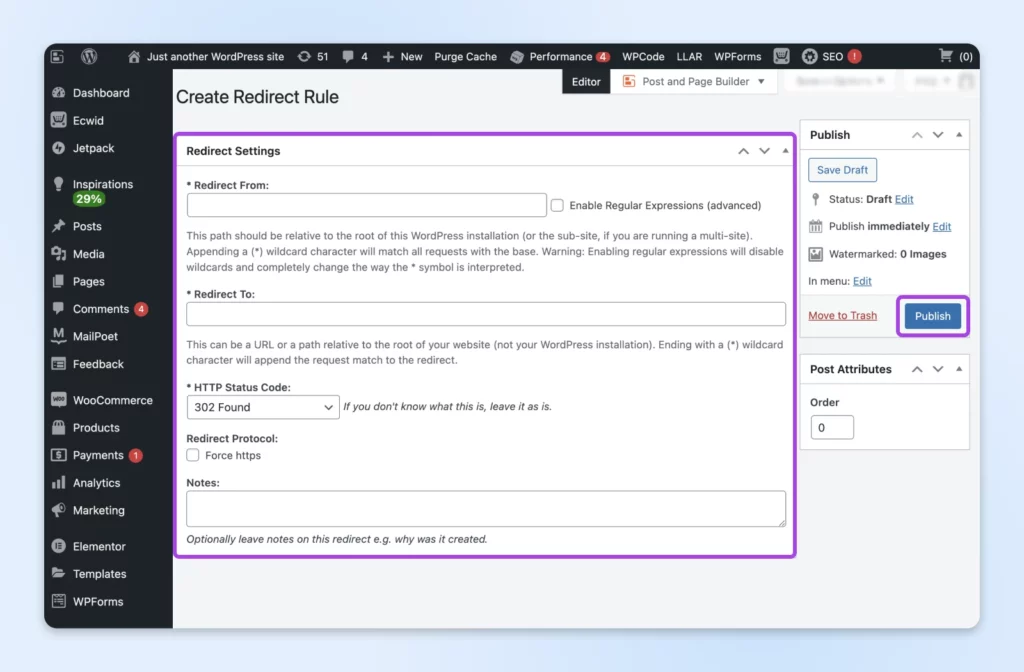
Enter the original URL path in the “Redirect From” field and the destination URL in the “Redirect To” field. Then, select your preferred HTTP status code (302 is temporary, 301 is permanent) and click the “Publish” button to activate your redirect.
If you want to take a deeper dive (and see some alternative routes), check out our dedicated guide to creating 301 Redirects in WordPress. The post also contains detailed instructions on editing your .htaccess file.
5. Check Your Links Manually
Well, what if you own a teeny tiny business website and you don’t need the hassle? Luckily, you can check your links manually in five easy steps:
- List your pages: Write down or open a document listing all the pages on your website.
- Click through every link: Start with the homepage and click every link, including navigation, footer, and in-text links. Open each link in a new tab to see if it loads properly. Repeat for every page of your site.
- Check for errors: If a page doesn’t load, note the error (e.g., “404 Not Found” or “This site can’t be reached”). If the link goes to another site, make sure the page is still active and relevant.
- Record issues: Keep a simple spreadsheet (or a notes app) where you list broken links and where they appear on your site.
- Fix or remove: If the broken link is internal, check if the page has moved and update the link. If it’s an external link, find a new relevant source or remove the broken one.
This should only take you a couple of hours if you run a small website. Just don’t get distracted; it’s way too easy to start fixing links on the fly, and forget to check the other parts of your site!
Internal vs. External Broken Links
The best fix for each broken link depends on whether it’s internal (pointing to your own content) or external (pointing to another site).
As a general rule:
- Internal links: Update the broken link with the new URL, unless you deleted the original content.
- External links: Find another resource that performs the same role as the lost page, or delete the link completely.
Fixing the Ongoing Problem of Broken Links
Of course, finding and fixing all the broken links on your site isn’t a one-time job. As time passes, links will continue to break. So, how do you keep up?
That’s where dedicated tools really make the difference. Most allow you to schedule regular broken link checks. Some can even alert you when they find a new issue.
This feature is often a premium option. It might not be worth paying for if your site is pretty small. But if you have loads of pages, we recommend setting up periodic checks.
Marketing Hack: Fix Broken Links on Other Websites
Broken links don’t only affect your site. Every website has them.
If you find broken links on other sites, you have the chance to make some moves in SEO.
Broken link building is a marketing hack used by many SEO professionals. It works like this:
- Use link-checking tools to find broken links on notable websites.
- Get in touch with the site owner and suggest your content as the perfect replacement for a specific broken link.
- They add a link to your site, boosting your domain authority.
Boom, instant high-quality backlinks!
Well, it’s not instant. You might have to email a lot of site owners before you get a response. But the rewards can be worth the effort.
More Resources on Essential Website Maintenance
Want to keep on top of other website maintenance tasks? Here are some of our most popular guides:
Fix Your Business Website Today
We did it. Your customers no longer feel ghosted; they can see you care about making this work.
Just as importantly, fixing your links is going to push your site up the search rankings and help you close more sales. If that wasn’t reason enough to check for broken links, we give up.
¯_(ツ)_/¯
Remember, your options are to:
- Use a dedicated dead link checker.
- Grab a WordPress plugin for checking links.
- Visit your Google Search Console dashboard.
- Set up 301 redirects.
- Manually check and fix your links.
While you’re thinking about improving your website, why not upgrade your hosting? Our plans offer unlimited bandwidth and 100% guaranteed uptime, so you’ll never leave your customers high and dry.
Sign up today to feel the difference!

Get More Website Traffic
We take the guesswork (and actual work) out of growing your website traffic with SEO.
Did you enjoy this article?

